Fractional Farrow Delay Filter
In signal processing, the need sometimes arises to nudge or fine-tune the sampling instants of a signal by a fraction of a sample, for example aligning multi-channel data in smart grid applications. An FIR Farrow delay filter is typically employed to achieve this task, and may be combined with a traditional integer delay line in order to achieve a universal fractional length delay line.
A Fractional delay based on an FIR Farrow structure may be defined as:
\(H(z)=(1-\alpha)+\alpha z^{-1}; \; 0 \leq \alpha \leq 1 \)
Which produces a fractional linear delay of \(\alpha\) between 0 and 1 samples. However, a more universal building block can be achieved by combining the Farrow delay structure with an integer delay, \(\Delta\)
\(H(z)=(1-\alpha) z^{-\Delta}+\alpha z^{-(\Delta+1)}\)
The plot shown below shows the magnitude (blue) and phase (purple) spectra for \(\Delta=9, \, \alpha=0.52\). As seen, the fractional delay element results in a non-flat magnitude spectrum at higher frequencies.
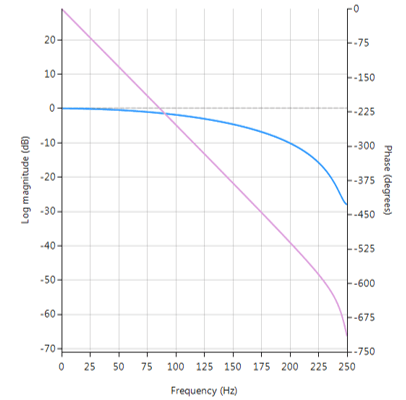
Frequency reponse of Farrow delay filter.
Implementation
A Farrow delay filter may be implemented in ASN FilterScript as follows:
[code language=”java”]
ClearH1; // clear primary filter from cascade
interface alpha = {0,1,0.02,.5}; // fractional delay
interface D = {1,30,1,10}; // integer delay
Main()
Num = {zeros(D),1-alpha,alpha}; // numerator coefficients
Den = {1}; // denominator coefficient
Gain = 1/sum(Num); // normalise gain at DC
[/code]